Ready to transform your vocal mixes?
Dive into our comprehensive female vocal eq cheat sheet.
Uncover the art of sculpting captivating female voices with easy-to-follow instructions.
Learn how to address muffled tones, enhance presence, and more.
As a bonus, we've condensed the key takeaways into a practical "Cheat Sheet" for instant application.
Elevate your tracks from ordinary to extraordinary.
Female Vocal EQ Cheat Sheet
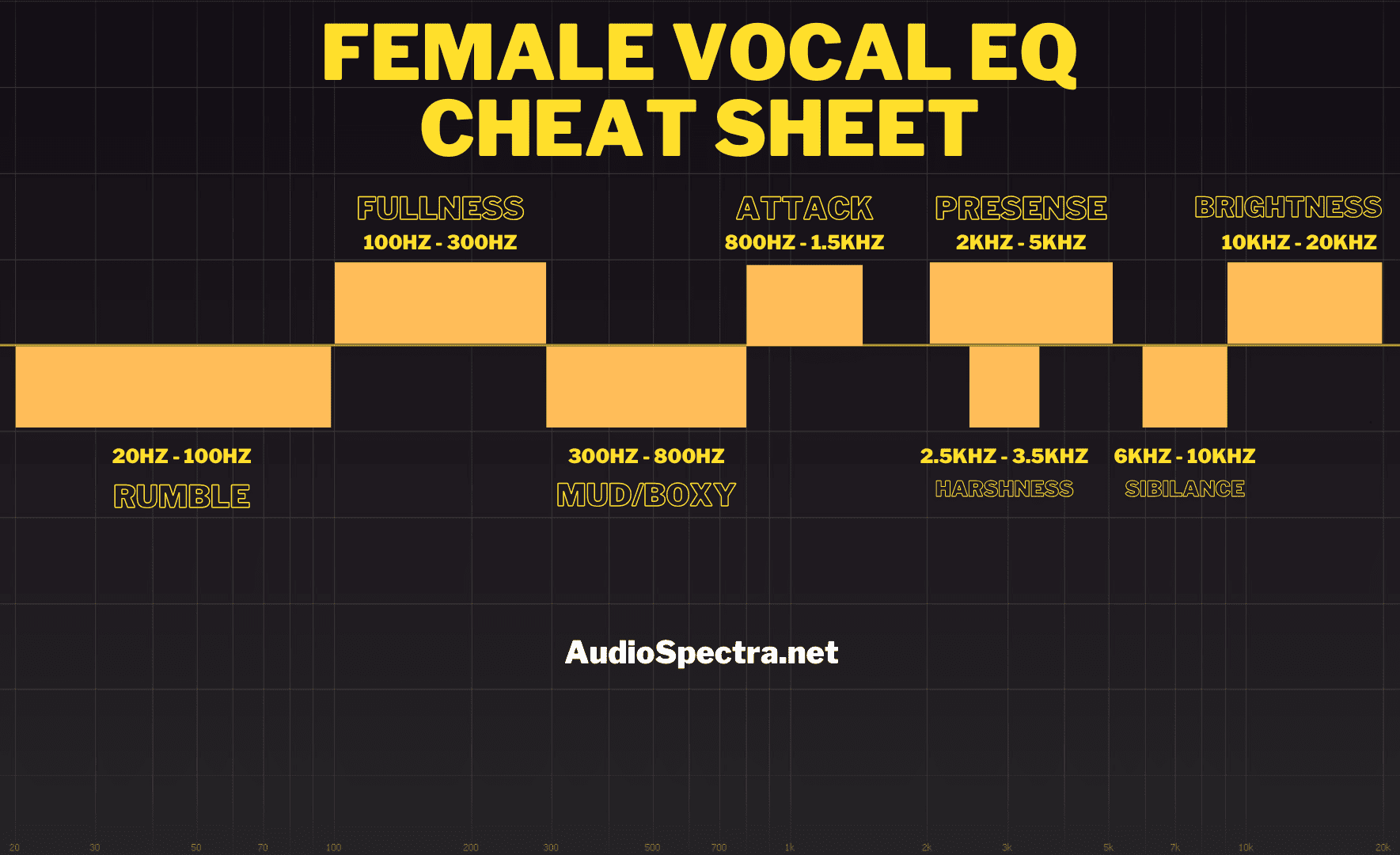
Having learned various EQ techniques for the female voice, this vocal EQ cheat sheet provides a quick reference to enhance your workflow:
- High-Pass Filter: Start at 80 Hz and adjust to clear low-end muddiness.
- Sibilance Control: Use a narrow Q (6 kHz–10 kHz) to reduce "s" and "sh" harshness.
- Boost Presence: Gentle lift (2 kHz–5 kHz) for clarity without harshness.
- Tame Mud or Boxy Tones: Cut frequencies (400 Hz–800 Hz) to smooth vocals.
- Taming Resonances: Use narrow Q to cut problematic frequencies in the midrange.
- Add Air and Sparkle: Boost above 10 kHz for brilliance; be subtle.
Remember, small adjustments yield natural results.
Listen carefully and A/B test changes. Practice and experimentation will refine your EQ skills over time.
Trust your ears to sculpt captivating female vocals that stand out in any mix.
How To EQ Female Vocals Professionally

Using EQ on vocals is crucial in music mixing.
EQ empowers you to sculpt vocals, ensuring they cut through the mix and shine, while neglecting EQ can result in lackluster and compromised vocal performances.
Enough talk; let’s dive into the practical techniques.
- High-Pass Filtering for Low-End Cleanup
To keep female vocals clear and focused, start with high-pass filtering.
This technique trims unnecessary low frequencies that might clutter the low end of a mix.
Set the high-pass filter at around 80 Hz as a starting point.
Gradually increase the cutoff frequency while listening for any negative impact on the vocals.
The goal is not to eliminate all low frequencies but to strike a balance that maintains the vocal’s warmth while reducing boominess and rumble.
By removing excess low frequencies, you create more space for bass instruments and prevent the mix from becoming congested.
- Dealing with Sibilance and Harsh Frequencies
Sibilance, those sharp “s” and “sh” sounds, can make vocals sound harsh.
Listen carefully to identify these problem areas.Use a narrow Q-band, focusing around 6 kHz to 10 kHz. Gently reduce sibilant frequencies without dulling the vocals.
Harshness around 2 kHz to 5 kHz can also make vocals piercing. Apply a wider Q setting to this range.
Carefully decrease the harsh frequencies, maintaining a balance between clarity and smoothness.
Balancing sibilance and harshness is vital for an enjoyable vocal mix.
Aim for a natural sound that doesn’t cause listener fatigue.
- Boosting Presence and Clarity
Enhancing the presence and clarity of female vocals brings them to the forefront of the mix.
Boosting frequencies between 2 KHz and 5 KHz achieves this effect. A gentle lift in this range adds brightness without sounding unnatural.
Avoid excessive boosts, as they can create an overly bright or harsh sound. Small adjustments often yield more natural results.
The boosted frequencies enable the vocals to cut through the mix, making them more intelligible without overpowering other instruments.
Presence and clarity ensure that vocals don’t get lost in the arrangement.
Strive for a balanced blend where vocals shine without becoming too edgy.
- Controlling Nasal or Boxy Tones
Nasal or boxy tones can affect the naturalness of the vocals.
These unwanted frequencies often sit around 400 Hz to 600 Hz. To address them, apply gentle cuts in this frequency range.
Listen attentively to identify the nasal or boxy quality of the vocals.
Gradually reduce the frequencies causing these issues. Be cautious not to overcut, as this can lead to a hollow sound.
The goal is to maintain the warmth of the vocals while minimizing unwanted coloration.
Subtle adjustments in the nasal or boxy frequency range result in a smoother vocal texture.
- Taming Unwanted Resonances
Unwanted resonances in female vocals can cause unevenness and harshness.
These resonances often appear in the midrange. Use a narrow Q setting on your EQ to target these frequencies precisely.
Listen closely to identify the resonant frequencies that need taming.
Gradually cut them while monitoring the effect on the vocals.
Be cautious not to overcut, which might lead to a thin or unnatural sound.
Taming resonances requires patience and attentive listening. Make subtle adjustments, checking how each cut affects the overall vocal tone.
With practice, you’ll refine your ability to control resonances, resulting in smoother and more balanced vocals that fit harmoniously within the mix.
- Final Touch: Adding Air and Sparkle
Adding a touch of airiness and sparkle elevates vocals in the mix.
To achieve this, gently boost frequencies above 10 kHz. This adds brilliance without sounding overly bright.
Carefully listen while making the boost. Small adjustments are key, as excessive boosts can introduce unwanted sibilance.
The goal is to enhance the vocal’s top-end without making it harsh or piercing.
The air and sparkle boost give vocals a captivating quality, making them more engaging to listeners.
Advanced Techniques

As you've honed your EQ skills in the realm of female vocal mixing, it's time to explore advanced techniques to elevate your prowess to the next level.
These techniques offer refined control over vocal presence and spatial characteristics, allowing you to sculpt captivating mixes that stand out with both technical finesse and creative flair.
a. Multiband EQ for Dynamic Control
Multiband EQ allows targeted adjustments to specific frequency ranges.
Apply it to address complex tonal issues.
For instance, if a female vocal track exhibits unevenness across multiple frequency bands, use multiband EQ to shape the sound more precisely.
Identify problem areas and assign different frequency bands for adjustments.
This technique offers finer control, helping you sculpt the vocal's tone while maintaining its natural timbre.
However, be cautious not to overuse it, as excessive adjustments can lead to an artificial sound.
b. Mid-Side EQing for Widening Vocals
Mid-Side EQing enhances vocal width in the stereo field.
Boosting the sides gently around the presence frequencies (2 kHz to 5 kHz) can make vocals feel wider without affecting the center.
This widens the vocal image while keeping its core intact.
Avoid excessive side boosting, as it may compromise mono compatibility.
Subtle adjustments create a pleasing sense of space while preserving the mix's mono compatibility for different playback systems.
c. Dynamic EQ for Smoother Tonal Adjustments
Dynamic EQ is a hybrid of EQ and compression.
It reacts to changes in the input signal, making it useful for controlling harsh peaks or resonances dynamically.
If a female vocalist sounds harsh during certain phrases, using dynamic EQ on the voice can tame those moments without affecting the rest of the performance.
Identify the problematic frequencies and set up the dynamic EQ to react only when those frequencies exceed a certain threshold.
This technique ensures that the voice retains its natural qualities while staying consistent in tone throughout the performance.
As you explore these techniques, remember to exercise restraint and let the mix guide your choices.
FAQ:
What frequency is female vocals?
Female vocals typically encompass a range of frequencies from around 165 Hz to 255 Hz for lower notes and extend up to approximately 1.5 kHz to 2.5 kHz for higher notes.
This frequency range captures the warm richness of lower registers and the bright clarity of higher tones in female voices.
Adjusting EQ within this spectrum can enhance the distinct character and presence of female vocals in a mix.